Your Guide to the Essential Electrical Junction Box
An Electrical Junction Box is one of the most fundamental components in any modern electrical system, yet its importance is often overlooked. These enclosures, typically made of metal or plastic, serve a critical purpose: to safely house and protect electrical connections. Whether in a residential home, a bustling commercial building, or a heavy-duty industrial facility, the proper use of a junction box is non-negotiable for safety, compliance, and system longevity. It prevents short circuits, shields wiring from environmental factors like dust and moisture, and provides a secure point for wires to be joined together. Without these vital enclosures, electrical systems would be hazardous, unreliable, and incredibly difficult to maintain. This comprehensive guide will delve into every aspect of the electrical junction box, from its various types and materials to detailed installation procedures and safety standards, ensuring you have the knowledge to handle your next project with confidence and precision.
Understanding the role of an electrical junction box is the first step toward appreciating its necessity. Essentially, it acts as a central hub where multiple wires or cables converge and are connected. This prevents the tangled, hazardous mess of exposed wires and ensures that each connection is secure and protected. Furthermore, these boxes provide a barrier against accidental contact, which could lead to electric shock, and they contain sparks or heat from a faulty connection, significantly reducing fire risk. As we explore the world of electrical components, you’ll see how EPCOM provides not just the enclosures themselves, but a full ecosystem of products designed to work together for a flawless and safe installation.
Exploring the Different Types of Electrical Junction Boxes
The specific needs of an electrical project dictate the type of junction box required. Factors such as location (indoor vs. outdoor), the number of connections, and the type of wiring all play a role in the selection process. Using the wrong type of box can compromise safety and lead to code violations. Therefore, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the common varieties available on the market. EPCOM offers a wide range of solutions to meet the demands of any application, ensuring you always have the right component for the job.
The Durable Metal Electrical Junction Box
Metal electrical junction boxes, typically crafted from steel or aluminum, are renowned for their strength and durability. They are the preferred choice for applications where physical protection is paramount. For instance, in areas with exposed wiring, such as unfinished basements, garages, or industrial settings, a metal box provides superior protection against impact. Moreover, metal boxes are required when using metal-sheathed (armored) cable or metal conduit, as the box itself becomes part of the electrical ground path. This grounding feature is a key safety advantage, helping to protect against faults. While they are incredibly robust, it’s important to note that standard steel boxes are intended for indoor use only, as they can rust if exposed to moisture unless specifically treated or coated for outdoor environments.
Versatile Plastic Electrical Junction Boxes
Plastic junction boxes, most commonly made from PVC or fiberglass, offer a lightweight and cost-effective alternative to their metal counterparts. One of their primary advantages is that they are non-conductive, which eliminates the need for them to be grounded. This can simplify the installation process. Plastic boxes are exclusively used with non-metallic sheathed cable (like Romex). They often come with built-in cable clamps, making the process of securing wires quick and easy. While they don’t offer the same level of impact resistance as metal boxes, they are rustproof and corrosion-resistant, making them a suitable choice for damp indoor locations like bathrooms or laundry rooms, provided they are not exposed to direct weathering.
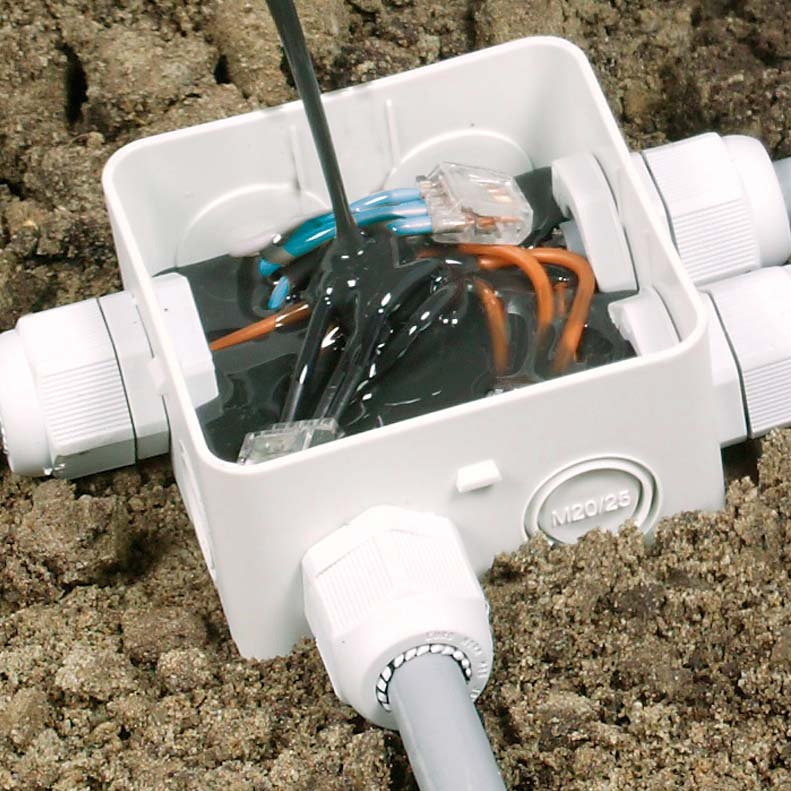
Outdoor and Weatherproof Electrical Junction Box Solutions
When electrical connections are needed outdoors, a standard indoor box simply won’t suffice. This is where the weatherproof electrical junction box comes into play. These specialized enclosures are designed to withstand the elements, protecting sensitive wiring from rain, snow, humidity, and dust. They are constructed with durable materials and feature gaskets, sealed seams, and watertight covers to ensure a secure seal. These are essential for outdoor lighting, outlets, and pool or spa equipment. When selecting an outdoor box, it’s critical to check its NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) or IP (Ingress Protection) rating, which indicates its level of protection against environmental factors. A higher rating signifies greater resistance to dust and water intrusion, ensuring a safe and long-lasting installation no matter the weather conditions.
Comparison of Junction Box Materials
Choosing the right material is a critical decision in any electrical installation. To simplify this choice, we’ve created a comparison table that highlights the key characteristics, advantages, and ideal use cases for the most common types of electrical junction boxes. Use this guide to ensure you select the best option for your specific project requirements, balancing factors like durability, cost, and environmental exposure.
| Feature | Metal Junction Box (Steel/Aluminum) | Plastic Junction Box (PVC/Fiberglass) | Weatherproof Junction Box |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durability | Excellent impact resistance. Very strong. | Good, but can crack under heavy impact. | High durability, designed to resist UV rays and extreme temperatures. |
| Conductivity | Conductive; must be grounded for safety. | Non-conductive; does not require grounding. | Varies (can be metal or plastic), but must be installed per code. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Standard steel can rust. Galvanized or aluminum options are better. | Excellent; will not rust or corrode. | Excellent; specifically designed to prevent corrosion from moisture. |
| Best Use Case | Indoors with metal conduit, exposed areas like garages or basements. | Indoors with non-metallic sheathed cable, behind drywall. | All outdoor applications, wet locations, and areas with high humidity. |
| Cost | Generally more expensive than plastic. | Very cost-effective. | Highest cost due to specialized construction and materials. |
A Step-by-Step Guide to Electrical Junction Box Installation
Proper installation of an electrical junction box is paramount for safety and functionality. While complex electrical work should always be performed by a qualified electrician, understanding the process is valuable for any property owner or project manager. This guide breaks down the fundamental steps, from preparation to final inspection. Remember to always comply with local building codes and turn off the power at the circuit breaker before beginning any electrical work. For reliable and safe connections, professionals trust EPCOM’s high-quality components every step of the way.
Step 1: Safety First – Preparation and Power Disconnection
Before you even touch a wire, your first priority is safety. Locate the main electrical panel and turn off the circuit breaker that supplies power to the area where you will be working. Use a voltage tester to confirm that there is no power flowing to the wires. Double-check to be absolutely certain. Gather all necessary tools and materials. A basic toolkit includes a drill, screwdrivers, wire strippers, and pliers. For making secure connections, a high-quality crimper is indispensable. For professional-grade results, consider using an electrical crimping tool from EPCOM, which ensures every connection is tight and reliable. Having everything on hand before you start will make the process smoother and safer.
Step 2: Mounting the Electrical Junction Box Securely
The junction box must be mounted securely to a firm surface, such as a wall stud, ceiling joist, or post. It cannot be left loose or hanging by the cables. For installations behind drywall, the box should be positioned so its front edge is flush with the finished wall surface. This is a requirement of the National Electrical Code (NEC) to ensure the box remains accessible and properly covered. Use the mounting holes or brackets provided with the box and secure it firmly with screws. An improperly mounted box can lead to strain on the electrical connections, creating a potential hazard over time.
Step 3: Running and Securing Wires
Next, run the electrical cables into the junction box. Each box has designated entry points, known as knockouts (on metal boxes) or ports (on plastic boxes). Remove only the knockouts you need to use. Each cable entering the box must be secured with a cable clamp, which prevents the wire from being pulled out and protects its sheathing from sharp edges. The NEC requires at least 1/4 inch of sheathing to be visible inside the box past the clamp. Inside the box, you should have at least 6 inches of free wire extending from the sheathing to provide enough length to work with comfortably and safely. For new wiring runs, it’s essential to use the correct type of wire for the application. High-quality THHN wire, known for its durability and heat resistance, is a superior choice for routing through conduit to your junction box, ensuring a safe and long-lasting installation.
Step 4: Making the Electrical Connections
This is the most critical step. Using your wire strippers, remove about 3/4 inch of insulation from the end of each individual wire (hot, neutral, and ground). Group the wires by function: all hot wires (usually black or red) together, all neutral wires (white) together, and all ground wires (bare copper or green) together. Connect the wires using approved connectors. While wire nuts are common, for many applications, especially with larger conductors or when tapping into an existing line, insulation piercing connectors offer a robust and time-saving solution. These connectors bite through the insulation to make a secure connection without the need for stripping, ensuring excellent contact and reliability. Ensure all connections are tight and secure. A loose connection can generate heat and poses a serious fire risk.
Step 5: Closing and Covering the Box
Once all connections are made, carefully fold the wires into the box. Be gentle to avoid straining the connections. According to regulations from safety organizations like OSHA, every electrical junction box must be covered with a matching, tight-fitting cover plate. This is a critical safety measure that protects the connections from debris and prevents accidental human contact. Never leave a junction box uncovered. Once the cover is securely fastened, you can restore power at the circuit breaker and test your work.
Advanced Considerations for Your Electrical Junction Box Project
Beyond the basics of installation, several advanced topics can significantly impact the safety and compliance of your electrical work. Understanding concepts like box fill, code requirements, and proper waterproofing techniques separates a standard installation from a professional-grade one. These considerations are vital for ensuring the long-term reliability and safety of your electrical system. Paying attention to these details helps prevent common issues and ensures your project will pass inspection.
Proper Sizing and the Importance of Box Fill Calculation
One of the most common mistakes in electrical work is using a junction box that is too small for the job. The National Electrical Code (NEC) has specific rules regarding “box fill,” which is the total volume occupied by wires, connectors, and devices within a box. Overcrowding a junction box is a serious fire hazard because it can lead to heat buildup and damage to wire insulation. The box fill calculation is based on the number and gauge of the wires, as well as any devices (like switches or outlets) and cable clamps housed within the box. Every junction box is stamped with its volume capacity in cubic inches. You must calculate the total volume required by your components and select a box that meets or exceeds that number. When in doubt, always choose a larger box to ensure ample space for wiring and heat dissipation.
Understanding Codes and Compliance
Adhering to electrical codes is not just a suggestion—it’s the law. The NEC provides the minimum standards for safe electrical installation in the United States. Local jurisdictions often have their own additional or modified requirements. These codes dictate everything from the type of junction box to use in a specific location, to how it must be mounted, and the methods for making connections. A primary rule is that all wire splices must be contained within an approved enclosure, like a junction box. Furthermore, that box must remain accessible after installation; you cannot cover it with drywall, paneling, or other permanent finishes. This ensures that the connections can be inspected and serviced in the future. For anyone working with electricity, resources from the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) can provide invaluable guidance on best practices and safety standards, complementing the dense language of official codebooks.
Why Professionals Choose EPCOM for Electrical Solutions
In the electrical industry, reliability is not a luxury—it’s a necessity. Faulty components can lead to system failures, safety hazards, and costly repairs. This is why professionals and discerning project managers consistently turn to EPCOM. Our commitment to quality, innovation, and a comprehensive product line ensures that every aspect of your electrical project is supported by components you can trust. From the foundational junction box to the most advanced connectors, EPCOM provides an ecosystem of products designed for superior performance and safety.
At EPCOM, we understand that a successful project requires more than just a single part; it requires a system of components that work together seamlessly. Our extensive catalog includes not only a diverse range of electrical junction boxes for any environment but also the high-grade wires, precision tools, and innovative connectors needed to complete the job to the highest standard. By choosing EPCOM, you are not just buying a product; you are investing in a promise of quality, durability, and unwavering support, ensuring your electrical systems are safe, compliant, and built to last.
Conclusion: The Cornerstone of a Safe Electrical System
The humble electrical junction box is truly the cornerstone of any safe, reliable, and compliant electrical system. It is a critical safety device that protects wiring, prevents fires, and guards against electric shock. From choosing the right type and material to ensuring a meticulous, code-compliant installation, every step is vital for the integrity of the entire system. By understanding the principles of proper junction box selection and installation, and by utilizing high-quality components and tools from a trusted supplier like EPCOM, you ensure that your electrical projects are not only functional but also fundamentally safe. Never underestimate the importance of this essential enclosure—it is the silent guardian of your electrical connections.

